Facts, Function, and Diseases of the Ear

Facts, Function, and Diseases of the Ear
The ear is much more than a hearing organ. It is a complicated set of elements that allows humans to hear and walk.
What is the size of a human ear?
Ears occur in a variety of forms and sizes. Men’s ears are larger than women’s.
The average ear is 2.5 inches (6.3 cm) long, with an earlobe that is 0.74 inches (1.88 cm) in length and 0.77 inches (1.96 cm) wide, according to the researchers. They also discovered that the ear grows more prominent with age.
Researchers in Germany, for example, revealed in Anthropologischer Anzeiger: Journal of Biological and Clinical Anthropology in 2007 that women’s ears grow less than men’s ears.
The highest ear length in the study for a 20-year-old woman was 2.4 inches (6.1 cm), but it increased to 2.8 inches (7.2 cm) for women over 70.
This length was 2.6 inches (6.5 cm) in men at the age of 20 and 3 inches (7.8 cm) in people over 70.
This finding was supported by a second study from Texas Tech University. The study discovered that ear diameter rises by 0.51 millimetres each year on average with ageing, most likely due to collagen changes.

The relationship between age and ear circumference can be represented mathematically: ear circumference in mm = 88.1 + (0.51 x age of the person).
In contrast, the circumference of the ear can be used to compute a person’s age using the equation: age of the person = 1.96 x (ear circumference in mm – 88.1).
How do the ears function?
The three ear sections are the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. They all provide various but vital tasks in terms of hearing and balance.
How does hearing work?
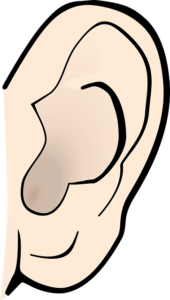
The auricle, or pinna, is a part of the ear, is the outer ear, consisting of a cartilage and skin loop on the outside of the skull. It works similarly to a megaphone.
According to Nebraska Medicine, sound waves are carried through the outer ear and sent into the external ear canal.
When looking at an ear up close, the ear canal is the visible section of the ear opening.
When sound waves strike the thin layer of connective tissue, it vibrates like a drum struck by a drumstick.
After passing through the eardrum, the vibrations enter the middle ear, also known as the tympanic cavity.
According to the Encyclopedia Britannica, the tympanic cavity is coated with mucous membrane and filled with air. The ossicles are three tiny bones termed the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup).
Bones vibrate when they move, according to the National Library of Medicine. The blood vessels dilate the stapes pushes a structure called the oval window in and out (NLM).
This action is transferred to the inner ear and cochlea, a fluid-filled spiral structure containing the spiral organ of Corti, the hearing receptor organ.
This organ’s tiny hair cells transform vibrations into electrical impulses conveyed to the brain via sensory nerves.
How the ears aid in balancing
The Eustachian tube, also known as the pharyngeal tube, balances the air pressure in the middle ear with the atmospheric pressure. This procedure assists people in maintaining their equilibrium.
Because it contains receptors that regulate the perception of balance, the vestibular complex in the inner ear is also vital for balance.
The vestibulocochlear nerve transmits sound and balance information from the inner ear to the brain.
Diseases and disorders of the ears
The ear is a delicate organ that injury, bacteria can harm, or simply environmental changes.
According to the NLM, ear infections are the most prevalent condition in newborns and young children.
Common symptoms of ear infections include discharge from the ear, hearing loss, ear pain, fever, headache, pain in the ear, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Meniere’s disease is an inner ear ailment caused by fluid issues in the ear.
Hearing loss, pressure or pain, dizziness, and tinnitus are symptoms. Tinnitus is defined as ringing in the ears.
Loud noises, drugs, and a range of other factors can also contribute to it.
According to the National Library of Medicine, barotrauma is ear damage caused by air or water pressure changes. It usually happens on aeroplane rides, high-altitude travel, or diving into deep waters.
Pain, plugged ears, hearing loss, and dizziness is some of the symptoms. Barotrauma is typically eased by “popping” the ears by yawning, chewing gum, or attempting to blow outside with the nose closed and the mouth closed.
Earwax, commonly known as cerumen, is antimicrobial and lubricates and protects the ear.
According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology, normal quantities should not bother most people, although earwax can accumulate and should be removed on occasion. Earwax symptoms include ear congestion, coughing, odour, discharge, itching, and hearing loss.
Hearing impairment
Hearing loss is not limited to the elderly. Hearing loss in both ears affects two to three out of every 1,000 newborns born in the United States.
15% of adults in the United States aged 18 and up have a hearing problem.
Nonetheless, according to the NIDCD, age is the most critical predictor of hearing loss in adults aged 20 to 69. Hearing typically declines with age, though ear injury can induce hearing loss at a very young age.
We are typically hooked to phones and music players for hours on end. When we expose our ears to hazardous noise, the sensitive cells in the inner ear are harmed. Regrettably, this harm compounds over time.
Increasing ear health
Hearing can’t be healed naturally once it’s been damaged. Most patients who have hearing loss require surgery or hearing aids. “The good news is that this is completely avoidable,” Cherukuri explains. “When utilising earplugs or headphones, I urge that my patients follow the 60-60 rule: no more than 60% of full volume for more than 60 minutes at a period.”
People who participate in loud activities or hobbies, such as athletic events, music concerts, shooting sports, motorcycling, or lawn mowing, should use earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones to protect their hearing.
Brushing carefully is another technique to avoid hearing loss and damage. The American Academy of Otolaryngology suggests using a cloth to clean the outer ear.
After that, add a few drops of mineral oil, baby oil, glycerin, or commercial drops in the ear to soften the wax and make it easier to drain.
A few drops of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide may also aid in healing. Never put anything in your ear.